
Many buyers assume that when the Federal Reserve cuts interest rates, mortgage rates will drop automatically. While the Fed’s decisions can influence mortgage rates, they are not directly linked. Here’s what actually affects mortgage rates:
Inflation plays a major role in determining mortgage rates. When inflation is high, lenders demand higher interest rates to protect their returns. This is why rates rose sharply in 2022 and 2023 as inflation soared.

Mortgage rates are closely tied to the yield on the 10-year U.S. Treasury bond. When bond yields rise, mortgage rates tend to go up as well. Investors’ expectations for economic growth, inflation, and Fed policy all affect bond yields, which in turn influence mortgage rates.
The Federal Reserve sets the federal funds rate, which affects short-term interest rates. While mortgage rates don’t move in lockstep with the Fed’s rate, markets react to Fed announcements, which can cause fluctuations in mortgage rates. The Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System is responsible for the discount rate and reserve requirements. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) holds eight regularly scheduled meetings per year. The next meeting is scheduled for next week.
Lenders adjust mortgage rates based on risk. If the economy is uncertain, lenders may raise rates to compensate for potential borrower defaults. Additionally, when demand for mortgages is high, lenders don’t have to compete as much on rates.
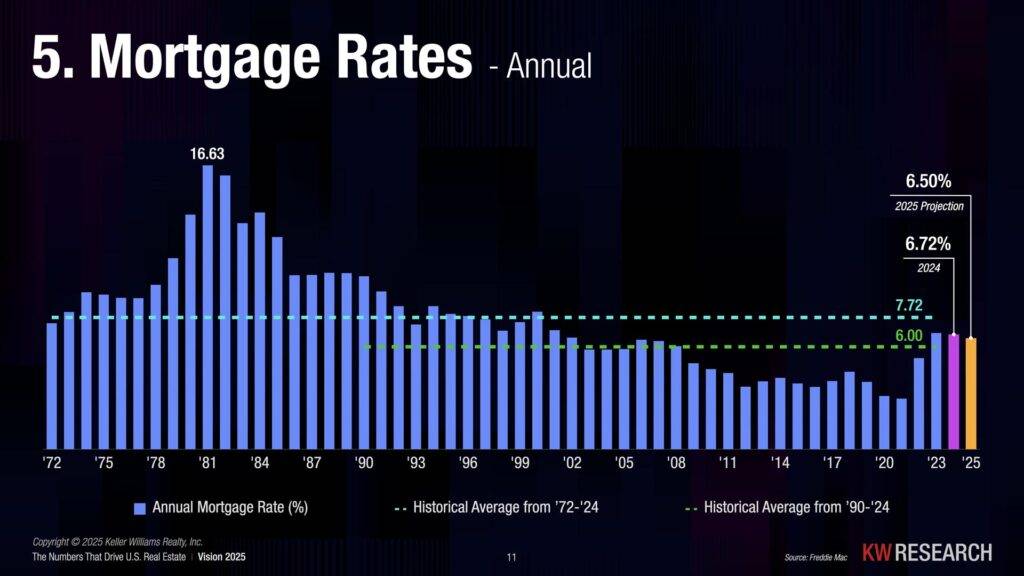
Many potential buyers remember the record-low mortgage rates of 2020 and 2021, when 30-year fixed rates dropped to 2-3%. However, these rates were not the norm. Historically, mortgage rates have been much higher:
With current mortgage rates around 6-7%, they are still below historical highs, though higher than the unusual lows of the pandemic era. Many experts believe that rates are unlikely to return to 2-3% anytime soon, as those conditions were driven by emergency economic policies that are no longer in place.
While it’s tempting to wait for lower rates, this strategy comes with risks. Here’s why buying now could be a smarter move:
Even if mortgage rates come down slightly, home prices may continue to rise due to strong demand and limited supply. A lower rate won’t help if the home you want becomes more expensive.
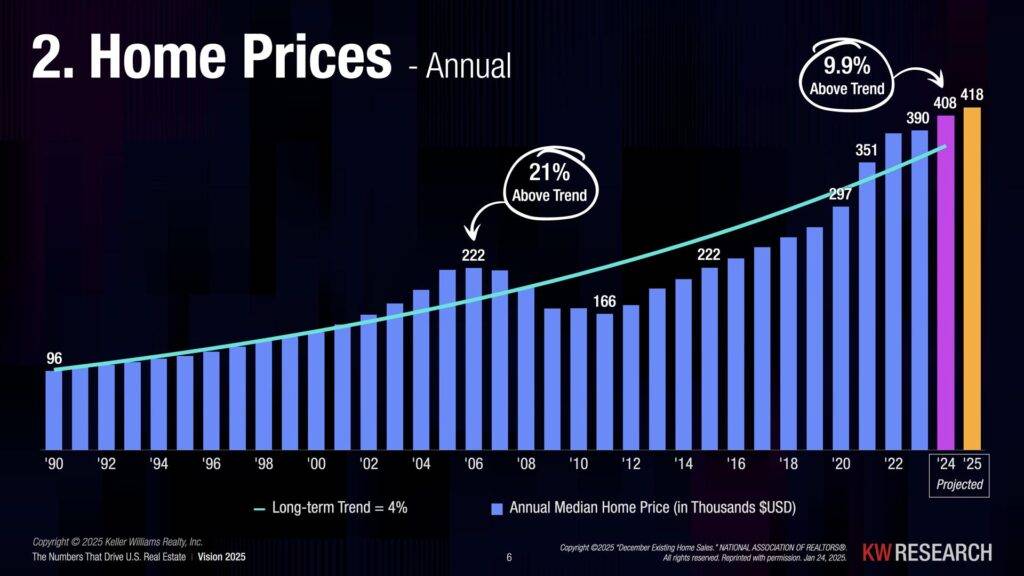
When mortgage rates decrease, more buyers enter the market, leading to bidding wars and higher home prices. In some cases, this can offset the benefit of a lower interest rate. If you have been waiting for rates to drop before you buy, remember, others have too.
If you buy a home at today’s rates and rates drop in the future, you may have the option to refinance to a lower rate. This allows you to take advantage of lower rates while benefiting from home appreciation in the meantime.
Buying a home now allows you to lock in a fixed monthly mortgage payment, providing stability. Rent, on the other hand, continues to rise, making homeownership a better long-term investment.
Mortgage rates are influenced by a variety of factors, and waiting for them to drop can be a gamble. While today’s rates are higher than the record lows of 2020-2021, they are still reasonable compared to historical averages. Instead of trying to time the market, buyers should focus on their personal financial situation, affordability, and long-term goals. If you find a home that meets your needs and budget, it may be wise to move forward rather than waiting for an uncertain future.
Disclaimer: All information contained in this web site is deemed reliable but not guaranteed. All properties are subject to prior sale, change or withdrawal notice. COMtnRealty.com believes all information to be correct but assumes no legal responsibility for accuracy.